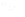Full Transparency
Our editorial transparency tool uses blockchain technology to permanently log all changes made to official releases after publication. However, this post is not an official release and therefore not tracked. Visit our learn more for more information.
By Vito Savino, general manager, DC Power Systems product line - GE Critical Power
When two powerhouse companies, such as Verizon and GE, come together to meet the challenge of energy efficiency and sustainability, the result is innovation. As leaders in telecommunications, data centers and energy, both companies share a commitment to improving energy sustainability – Verizon with its Sustainability Supplier Scorecard and GE with its ecomagination initiatives and energy-efficient technologies for the telecommunications market.
GE’s Critical Power “Eco Priority Source*” Delivers Alternative Power for Cellular Towers
In expanding its cellular service area, Verizon faced a challenge in deploying services in remote locations where utility power is either unreliable or unavailable. Typically, power in these locations is supplied, or supplemented, by generators using greenhouse-gas-emitting diesel or propane fuel. Fuel costs alone are generally 70 percent of the operating expense for a remote cell tower, and a generator running 24/7 leaves a large carbon footprint.
Verizon looked for new and energy-efficient ways to supplement cell tower power with solar and, eventually, wind power without compromising service reliability. The company teamed with GE’s Critical Power business on a key modular power system at five cell tower locations in California and Nevada by harnessing GE’s Infinity DC Power system with Eco Priority Source*. With an Eco Priority Source-enabled power system, a single power conversion module can be used to convert energy from multiple power sources (solar, generator or utility) – whatever is available at the site. The power conversion module is programmed to “smartly” adapt its response to match the power source.
A modular power system with ECO Priority Source capability will generally use renewable energy sources first, only using utility power or fossil-fuel-based generators as a supplemental energy source.

Verizon's Havasu Pass facility uses a solar-powered generator system.
The Verizon Havasu Pass facility in Needles, California, reduced generator runtime by 80 percent after being converted from a 30 kW propane-fired generator to a solar-powered Eco Priority Source-enabled system. By working together, Verizon and GE are delivering on sustainable solutions without compromising service reliability.
“Rectifying” Power Inefficiency at Telecommunications Central Offices
In 2010, Verizon and GE Critical Power teamed up with the United States Department of Energy (DOE) on a research project to take a bite out of the estimated $4.8 billion spent annually to power the information and communications technology industry in North America.
The result was the development and testing of a new class of energy-efficient rectifiers for telecommunications centers, with power-conversion efficiencies approaching 95 percent versus traditional 82 percent efficiency levels. Thousands of telecommunications central offices in the United States use traditional ferro electric rectifiers that provide power backup and convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This conversion creates heat and energy loss that also saps the energy required to keep equipment cool.
Verizon tested GE’s new high-efficiency switch mode rectifiers (SMRs) at five telecommunications central office locations across the country. The report to the DOE¹ showed that the facilities that converted from ferro electric to the new SMR units showed energy savings up to $7,000 annually.
The DOE research also extrapolated that if this new class of SMRs were deployed in the 25,000 telecommunications facilities in North America, estimated electricity consumption could be reduced by 400 million kWh with a corresponding 300,000 tons reduction of greenhouse gases.
Since 2012, GE and Verizon have deployed these high-efficiency rectifiers at Verizon telecommunications centers in eight states, with new SMR units creating both energy savings and reducing the dependence on fossil-fuel powered electric utility energy. According to Verizon, the energy-consumption differences between older, ferro electric rectifiers running at 82 percent conversion efficiency and GE SMR units performing at up to 95 percent efficiency can save up to 68,000 kwh/year of energy, resulting in cost savings of more than $7,000 annually.
GE and Verizon’s Shared Commitment on Greenhouse Gas Reduction
Both Verizon and GE share a common mission of working toward energy sustainability and conducting business in ways that protect our natural resources. GE’s active commitment to reducing greenhouse gases (GHGs) is an important part of that relationship.
As part of its ecomagination initiatives, GE has set clear goals for reducing the company’s GHGs, aiming to cut absolute GHG emissions by 25 percent by 2015 compared with 2004 levels. In 2013, at least 175 projects to optimize energy use were either completed or proposed for implementation across GE’s global operations. These projects should result in an estimated 100,000 metric tons of CO2 being eliminated from GE’s operations.
In February 2014, GE announced a new goal for GHG reductions through 2020. This new goal is a 20 percent absolute reduction from a 2011 baseline of operational GHG emissions, based on World Wildlife Fund and CDP’s “The 3% Solution,” methodology. The 3% Solution helps companies such as GE identify an emissions-reduction path and illustrates that corporations can profit while helping to stabilize the climate. By reaching the 20 percent reduction of operational GHG emissions goal, GE should achieve a 40 percent reduction in its carbon footprint from the original 2004 baseline.
Learn more about GE’s Critical Power business and GE’s ecomagination.
Notes:
(*) Indicates a trademark of the General Electric Company and/or its subsidiaries.
(1) DOE Study - # DE-EE0002891- High-Efficiency, Wideband Three-Phase Rectifiers and Adaptive Rectifier Management for Telecomm Central Office and Large Data Center Applications http://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/1044600.
The figures cited in this article unless otherwise noted, are based on industry-standard information or data collected by GE in the deployment of critical power systems. The results cited in this article are not a guarantee of performance or specific results, and individual results may vary based on specifications and operating conditions.